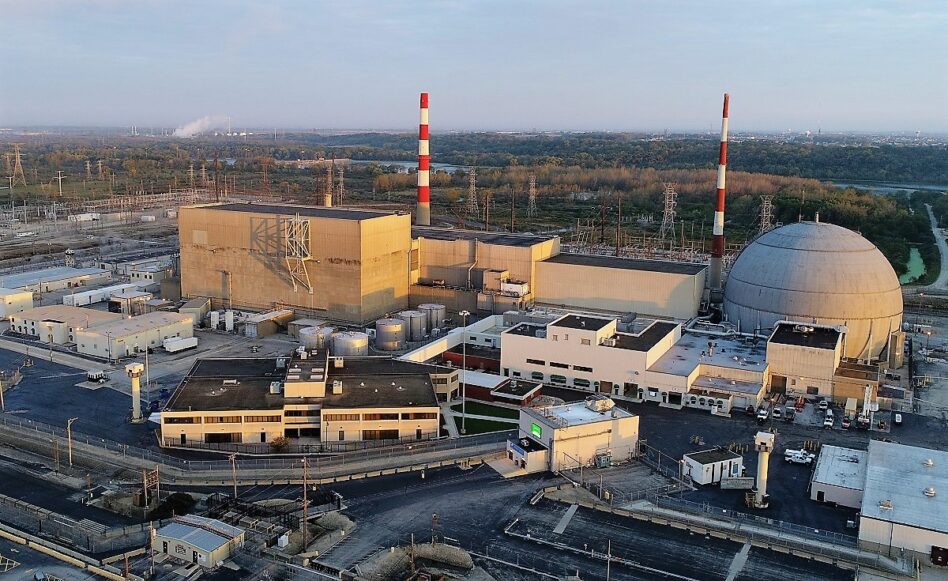
The US nuclear fleet is seeking a new lease on life. Constellation Energy, the nation’s largest nuclear operator, has filed two plant renewal applications with the NRC since the start of 2024, with more than half its fleet expected to follow suit over the next decade.
“We’re extending the lives of our existing sites to power the nation into 2060 and beyond,” Constellation CEO Joseph Dominguez said in a Q1 earnings call. “We’ve already received or have announced license extensions at five and have more to come, assuming supportive policy.”
Where old becomes bold: Clean energy generation provisions outlined in the Inflation Reduction Act, alongside consumer demand for sustainable power, have spurred investment in existing nuclear capabilities.
“I want to emphasize the most important thing right now that customers could do in this space is make sure the existing fleet we have right now is ready and funded for subsequent license renewals,” Dominguez said. Constellation runs 21 of the 94 operational reactors in the US, accounting for 19,000+ MW of capacity.
Renewal isn’t cheap: The overhead cost of a nuclear license renewal is in the tens of millions of dollars, Steve Nesbit, former president of the American Nuclear Society, told Ignition in an email. Though that seems like a hefty price tag, it’s still “a fraction of the cost of constructing a new plant,” Nesbit said.
Nesbit outlined key steps in the two- to three-year licensing process that contribute to expenses:
- Collecting required information and submitting it to the NRC
- NRC review fees
- Legal costs associated with Atomic Safety and Licensing Board hearings if the public intervenes
Nesbit noted that renewal decisions are on a case-by-case basis. Electricity demand and pricing vary nationwide, with reactors operating in both regulated and deregulated wholesale markets.
“The US will not attain its clean energy goals without a continued contribution from currently operating nuclear power plants, including power generated following license renewals,” Nesbit said.