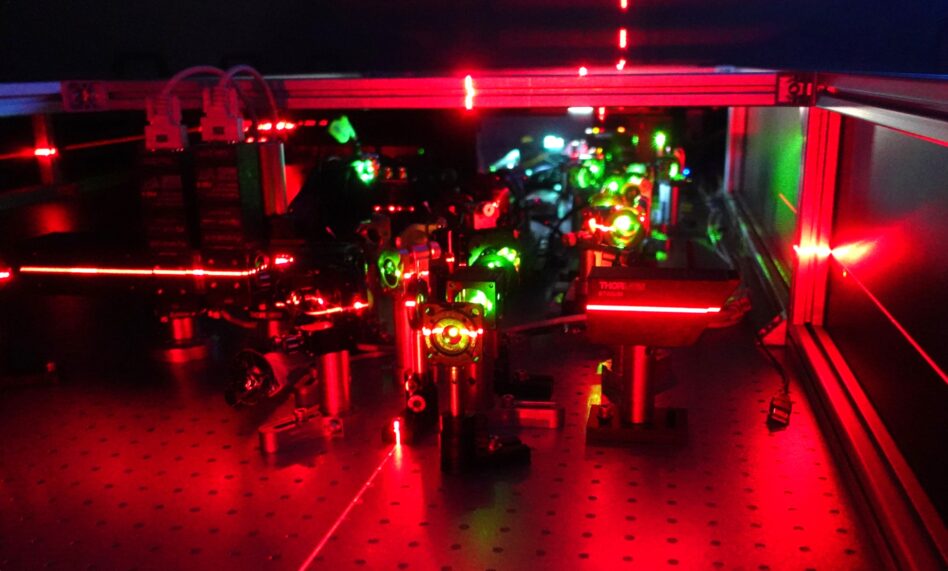
Tokamak Energy, a UK-based fusion company, is developing an updated laser measurement technology to improve its ST40 fusion machine.
“The extreme conditions created by the fusion process mean we need to perfect the laser-based diagnostics technology now to move forward on our mission of delivering clean, secure and affordable fusion energy in the 2030s,” said plasma physicist Tadas Pyragius in a release.
Tokamak Energy 101: The UK fusion firm is building a spherical tokamak (more on that in a sec) and aiming to build a commercial fusion plant to deliver electricity to the grid by the mid-2030s. It’s raised ~$258M to date, per PitchBook, and has secured grants and partnerships with a number of UK and US government agencies and national labs.
The company isn’t waiting until it has a fusion plant online to earn revenue, however. It’s gone to market with a superconducting magnet product that is supplementing its venture capital funding.
“We are now leveraging and commercializing those magnets in the near term,” Tokamak Energy US President Michael Ginsberg told Ignition. “In fact, in 2023, we had our first revenue with those, and in 2024, we’ve got millions of pounds of revenue forecasted.”
Tokamak Energy recently announced plans to scale up its US arm, too.
- These plans stem from DOE grant the company won last year, which awarded eight companies a total of $46M.
- Ginsberg said the company hopes to scale to ~20 US employees in the next year, “but it has to be justified by demand.”
Fast and steady: A tokamak is a category of fusion reactor that uses magnets to contain a superheated plasma within a donut-shaped system. Simply put, to make a fusion reaction occur, a tokamak will heat a gas of deuterium and tritium (both hydrogen isotopes) until the energy and density are intense enough that the atoms fuse, producing helium atoms and a spare neutron holding most of the energy produced in the reaction.
It’s a delicately balanced game to sustain the plasma. The tech unveiled by Tokamak Energy this week is designed to collect data on fuel density throughout the reaction, helping the team to iterate on the tokamak design in the push toward a commercial product.
- A company spokesperson said though the diagnostic system hsa commercial potential, the company doesn’t know yet whether it will sell it as a product.
+ Stay tuned: In a conversation with Ignition, Tokamak Energy’s Ginsberg dove into fusion’s place in the energy industry and how Tokamak Energy is thinking about revenue generation in the long lead-up to fusion reactor commercialization. A full Q+A is headed your way next week.
Note: A previous version of this story misstated the amount of the 2023 DOE grant received by Tokamak Energy. This error has been corrected.
Lead Reporter of Ignition